What is frailty?
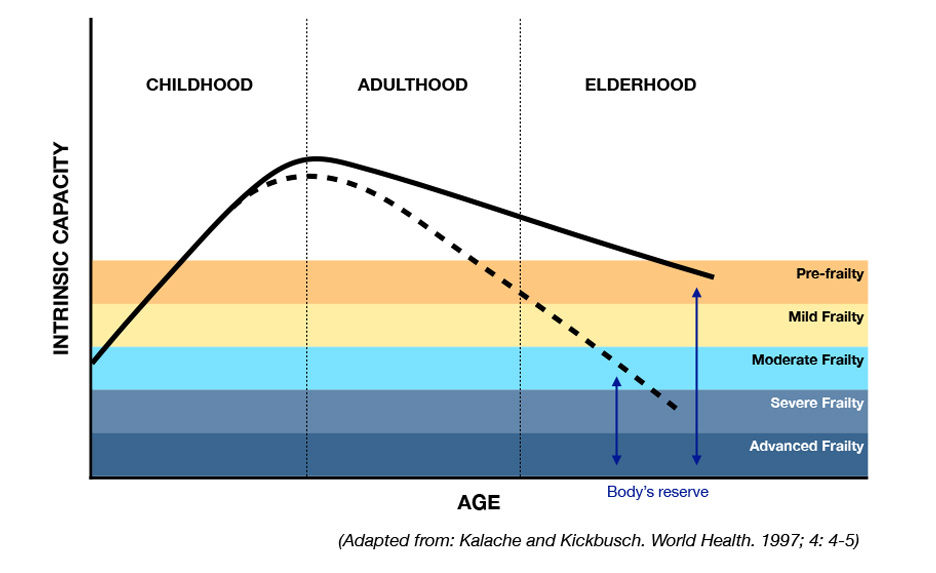
Frailty is a clinically identifiable state of vulnerability that results from the body’s loss in built-in reserves as age-related cellular and physiological changes accumulate
(Clegg et al. Lancet 2013,
Kim and Rockwood. New England Journal of Medicine 2024).
Two theories dominate the understanding of frailty: the Physical Frailty Phenotype, which characterizes frailty as a clinical syndrome arising from altered metabolism and abnormal stress responses
(Fried et al. Nature Aging 2021)
and the Deficit Accumulation Frailty, which considers frailty as a state of poor health resulting from deficits accumulating over time
(Howlett et al. Nature Aging 2021).
As frailty progresses, older adults are at a greater risk for falls, hospitalizations, loss of independence, nursing home admission, and death, even from small stressors, such as new medication, minor infection, or minor surgery.
Why is frailty important to measure?
- Older adults with frailty are responsible for nearly 50% of preventable Medicare spending (Figueroa et al. Annals of Internal Medicine 2017).
- Regularly measuring frailty scores over time can be useful for identifying individuals at increased risk of mortality and higher healthcare expenditure (Shi et al. The Journals of Gerontology Medical Sciences 2023).
- People with greater frailty are at a higher risk of developing age-related chronic conditions at an accelerated pace (Jang et al. JAMA Network Open 2023).
- Understanding frailty is crucial not only for providing individualized treatment and prognosis at the personal level but also for effective management of population health.
How to use frailty assessment to guide clinical care
- Understanding the patient’s frailty level on the fit-to-frail spectrum can be valuable for applying evidence from clinical trials and best practices in geriatric care. Note that the cut-off points for frailty assessment tools should be used as a guide, appropriately based on clinical assessment, and are not intended to be strict rules (Kim and Rockwood. New England Journal of Medicine 2024).

(From The New England Journal of Medicine, D.H. Kim and Rockwood K, Frailty in Older Adults, Vol. 391, Pages 538-548, Copyright © 2024 Massachusetts Medical Society. Reprinted with permission.)